This is part of the Med in Small Doses series, which aims to give you a snapshot of a disease or disorder. For information about the series, or common abbreviations click here.
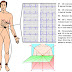
Anopheles mosquito infect humans with plasmodium.
PATHO: Mosquito → skin → liver → blood stream (merozoites) → attack RBCs → use haemoglobin → rupture cell → cycle continues
Types:
- P Vivax,
- P.Ovale,
- P.Malariae,
- P.Flaciparum (worse type)
- Infect RBC of any age
- Resetting & sequestration
- ↑ cytokine production
CFs: Fever, fatigue, jaundice, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, bloody stools
Severe Malaria: cerebral, severe anaemia, respiratory & renal failure.
Severe Malaria: cerebral, severe anaemia, respiratory & renal failure.
Complications: CHAPLIN
C erebral Malaria/Coma
H ypoglycaemia
A naemia
P ulmonary Odema
L actic Acidosis
I nfections
N ecrosis of Renal Tubules
Dx: well stained blood smear, ELIZA, PCR
Px: ↓ mosquito exposure, chemoprophalaxis (doxycycline, atovaquone+proguanil tablets), vaccine (in development)
Rx: Mefloquine cures 90 to 95% of P. falciparum malaria.
- Quinines, doxycycline – blood schizonticides
- Primaquine & Tafenoquine – tissue schizonticides
Checkout a Guide to Tropical Disease for some
epidemiology information on Malaria and other diseases.







No comments:
Post a Comment