Radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energy or waves travel through a medium or space. Wikipedia
Following the events occurring in Japan, there has been a greater interest in both the safety of nuclear reactors and the effects of radiation. The three critical components of determining the lethality of the radiation according to experts are;
- the intensity of exposure
- its duration
- and access to treatment
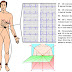
On RIANOVOSTI they have done up an infographic of the effects of radiation on the human body.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and Symptoms of radiation poisoning can be broken down into three main categories: hematopoietic, gastrointestinal and neurological/vascular.
- Hematopoietic - Decrease in blood cells which results in infections due to low white blood cells, bleeding due to low platelets, and anemia due to low red blood cells.
- Gastrointestinal - Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain.
- Neurovascular - Dizziness, headache, or decreased level of consciousness.
The most common form of treatment for exposure to Nuclear Radiation is Potassium iodide. Potassium iodide is only effective in protecting the thyroid and consequently only limits the likelihood of developing thyroid cancer.
Some other treatment options for radiation, with varying degrees of success include;
- Beta carotene
- Dihydroquercetin and sulfur
- Shark liver oil
- Modified citrus pectin
- Oligomeric proanthocyanidins
- Sodium alginate
The WHO have a list of recommendations for minimizing radiation exposure, available here.







No comments:
Post a Comment