This is part of the Med in Small Doses series, which aims to give you a snapshot of a disease or disorder. For information about the series, or common abbreviations click here. Run through how to perform gastrointestinal exam to refresh your memory, and link in clinical features.
Two major disorders: Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD)
There are other forms. Indeterminate IBD (10-15%)
Crohn's incidence rising. Higher incidence of IBD in Jews, less in Black/Hispanics.
PATHO:
- Genetics (better defined in CD); NOD2, ATG16L1, IRGM.
- Mucosal immune responses (not autoimmune).
- Epithelial defects: UC (ECM1) and CD (NOD2)
- Microorganisms: massive numbers
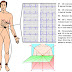
CFs: A PIE SACK - Extraintestinal manifestations.
A phthous ulcers
P yoderma gangrenosum
I ritis
E rythema nodosum
S clerosing cholangitis
Arthritis (Ankylosing Spondylitis)
C lubbing of fingertips
K idney
| CROHNS | UC | |
|---|---|---|
| Bowel Region |
Ileum/colon
|
Colon
|
| Distribution |
Skip Lesions
|
Continious/diffuse
|
| Wall |
Thick
|
Thin
|
| Uclers |
Deep
|
Superficial
|
| Fat/Vitamin Malsorption |
Yes
|
No
|
| Malignant Potential |
Yes
|
Yes
|
| Toxic Megacolon |
No
|
Yes
|
RFs: FHx (1st degree relative), Smoking (↓UC, ↑CD), Perinatal illness/health event.
Tx: Comparison Table - Wikipedia (IBD)
Wikipedia.com
IBD: surgery indications "I CHOP".
I nfection
C arcinoma
H aemorrhage
O bstruction
P erforation






No comments:
Post a Comment