This is part of the Med in Small Doses series, which aims to give you a snapshot of a disease or disorder. For information about the series, or common abbreviations click here.
International Prev. 0.5-1.0%. M = F. Males have worse outcomes.
CFs: A useful mnemonic is HD N CD. Think High Definition And CD.
H: hallucinations
D: delusions
N: Negative symptoms (flat affect, social withdrawal, poverty of speech)
C: catatonic or grossly disorganized behavior
D: Disorganized speech
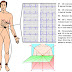
Positive
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- Disorganised behaviour
- Thought disorder
- Catatonia
Negative
- Social withdrawal
- Emotional flattening
- Anhedonia
- Reluctance to perform everyday tasks
PATHO: Genetic Factors (accounts for ~80%) & Environmental Factors play a role.
Cortex – atrophy, larger ventricles &↓temporal lobe volume
Limbic system – ↓ size of amygdala, hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus.
More marked on left side.
Thalamus – ↓ volume
Dx Criteria:
- Psychotic symptoms for over a month
- Impaired psychosocial function
- Continuous signs of illness for over 6 months
- Not explained by prominent mood disorder
Tx: Long-term planning & Family Education are important aspects.
Antipsychotics - Typical (e.g. Haloperidol & Flupenthixol) & Atypical (e.g. Clozapine & Risperidone)
Mood stabilisers (e.g. Lithium - 'Gold Standard'; or Clozapine) & Psychosocial therapy





No comments:
Post a Comment